Evolution of WEB :-
Web 1.0 :-
- Web 1.0 refers to the first stage of the World Wide Web evolution.
- In web 1.0 we could only read the content from the website.
- Personal web pages were common, consisting mainly of static pages hosted on ISP-run web servers, or free web hosting services.
Web 2.0 :-
- Web 2.0 is also called the participative social web.
- Interaction and collaboration with each other are allowed by Web 2.0
- Web 2.0 is an enhanced version of web 1.0.
- Features of web 2.0 :
- Free sorting of information, permits users to retrieve and classify the information collectively.
- Dynamic content that is responsive to user input.
- Information flows between the site owner and site users using evaluation & online commenting.
- Developed APIs to allow self-usage, such as by a software application.
- Web access leads to concerns different, from the traditional Internet user base to a wider variety of users.
Web 3.0 :-
- Web3, the future internet we’re moving towards, is a decentralized internet.
- Under Web3, the internet is shared online and governed by the collective “we,” rather than owned by centralized entities.
- The Web3 world is one that has open-source protocols at its foundation. Web3 is about rearchitecting internet services and products so that they benefit people rather than entities.
Summary
Web1: Read 📖
Web2: Read-Write 📖 🖊️
Web3: Read-Write-Own 📖 🖊️ 🔑
For more on web evolution [geeksforgeeks.org/web-1-0-web-2-0-and-web-3..
Blockchain :-
State Management
- Blockchain starts with Genesis block (First block of blockchain).
- For hashing function to create the the hash value of particular block we use hash value of previous block, timestamp, data inside that block, nonce.
- For genesis block we used hash value of previous block is 0.
- Bitcoin's genesis state happened in 2009 when the public network launched. Ethereum's Genesis State happened in 2015, when it launched.
- Every transaction on a blockchain modifies the global state that is replicated across all nodes.
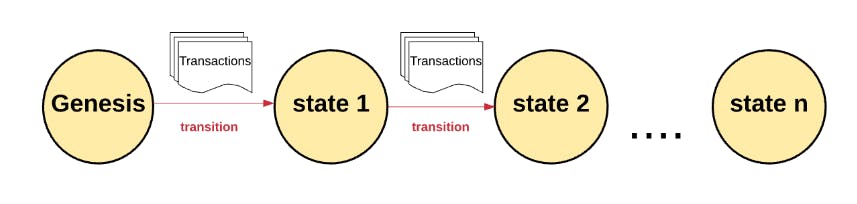
- As there are millions of transactions, transactions get grouped together in blocks. Hence we use the name of block(block number).
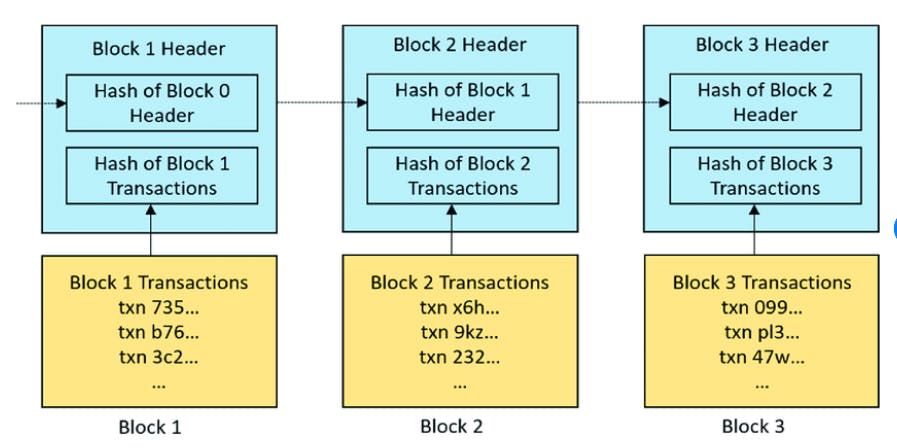
- These blocks are chained together in a cryptographically verifiable way so they are historically traceable.
Nodes
- Node in the blockchain is one of the computers that run the blockchain's software to validate and store the complete history of transactions on the network.
- A blockchain network is managed autonomously through a peer-to-peer distributed network of computer nodes.
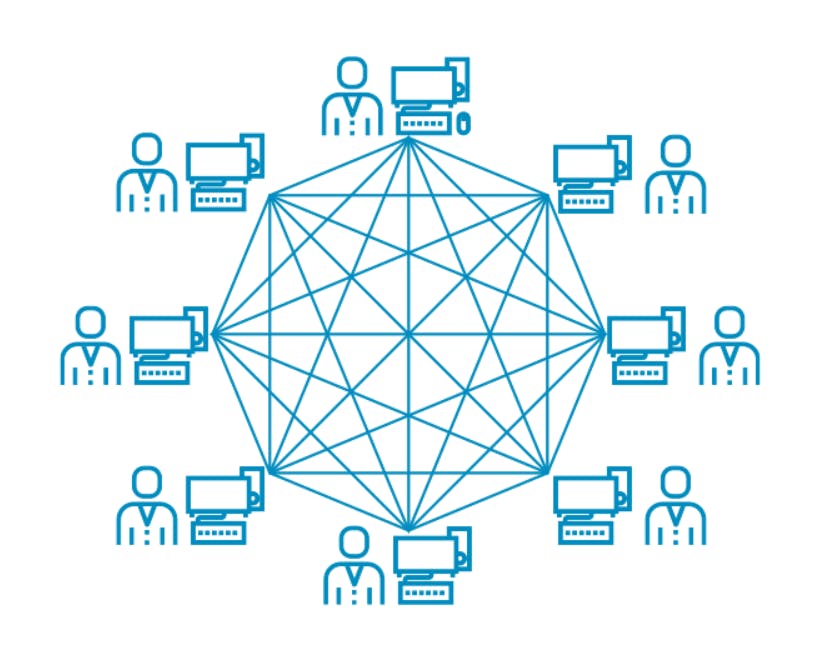
- Each node in the network keeps a copy of the global transaction ledger. Therefore, each node can individually verify and audit transactions happening on the network and ensure there was no illicit behavior.
- Another type of node is responsible for grouping together new transaction which are made in the network and put it in a block, verify them and propose the block to be included onto the global ledger by everyone else are known as Miners.
- Mining is computationally hard, and very important to do securely, so miners whose blocks get accepted are given a token reward for their hard work.
Decentralization
- Blockchain Technology works on decentralization.
- By storing data in a peer-to-peer network of nodes, the blockchain is a decentralized network.
It solves some traditional problems such as
- Data breaches in centralized systems expose lot of data.
- Centralized authorities can censor and shut down speech.
- Reliance on a central authority means upstream problems affect downstream consumers (e.g. AWS going down means most of the internet goes down with it).
Benefits of Decentralization are
- No censorship as it is not controlled by any centralized single authority.
- No downtime as there are 1000's of nodes across the globe present to run the network.
- Highly attack resistant making it infeasible to manipulate or destroy data.
Resources :-
Must Watch
Thank you for reading this blog it means a lot. I hope you understand some terms of Blockchain. In upcoming blogs I will share working of Blockchain. In this series of Blockchain next blog will be published on 12th September 2022.
Feel free to comment your thoughts and what things you want me to include. :)