Table of contents
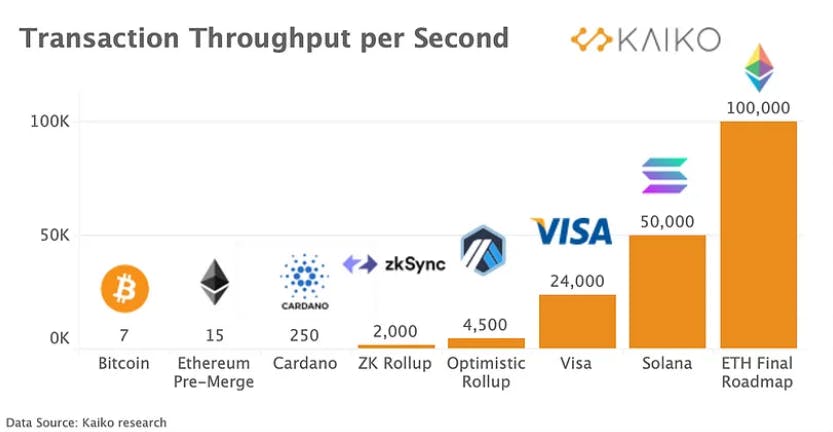
Day by day popularity of Ethereum is increasing hence the number of transactions per day increases and hence congestion is happening on the Ethereum network. If we want to go from one place to another we use highways that are multi-lane instead of single-lane roads. To avoid congestion we make multi-lane roads. Today Ethereum can do 15TPS(Transactions per second) and Bitcoin does 7TPS which is very less. For comparison mastercard does 5000TPS and visa does 24000TPS. Now you can compare and tell how slow ethereum is. If Ethereum wants to become the next internet then its TPS should be high. To solve this problem many solutions proposed let's discuss them.
Solutions
On-chain Scaling: In this method, developers proposed to scale the Ethereum chain through sharding.
- Sharding: Sharding is the process of splitting a database horizontally to spread the load. In an Ethereum context, sharding will reduce network congestion and increase transactions per second by creating new chains, known as “shards”. Sharding could ship sometime in 2023. Shards will give Ethereum more capacity to store and access data, but they won’t be used for executing code. We will learn more about sharding in detail in upcoming blogs.
A thread of Vitalik Buterin explaining the roadmap to scale Ethereum.
https://twitter.com/VitalikButerin/status/1312905882330521600
Off-chain Scaling: In this type of solution we don't need to modify the original existing Ethereum protocol. We add different blockchain layers to increase TPS and ultimately all these chains derive security from layer 1 Ethereum consensus only. We called them Layer 2 solutions. There are different layer 2 solutions. Other solutions involve the creation of new chains in various forms that derive their security separately from Mainnet, such as sidechains, validiums, or plasma chains.

Layer 2 Solutions: In this type of blockchain it derives its security from Mainnet Ethereum. There are three purposes of a blockchain 1. Data availability 2. Settlement layer 3. Execution layer.
These solutions only do Execution and Data Availability. Settlement happens on layer 1. Layer 2 is a collective term for solutions designed to help scale your application by handling transactions off the Ethereum Mainnet (layer 1) while taking advantage of the robust decentralized security model of Mainnet.
Types of Layer 2 Solutions :
Optimistic Rollups
Zero-Knowledge Rollups
We will discuss the concept of layer 2 and its different types in detail in upcoming blogs.
Disadvantages of Layer 2:
May remove liquidity from the primary blockchain
Potential security and privacy vulnerabilities.
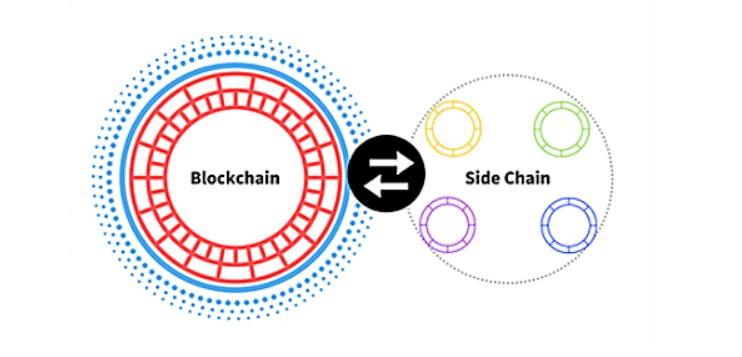
- Sidechains: Sidechains is an independent EVM-compatible chain that runs in parallel to the main Ethereum blockchain. These are compatible with Ethereum's main blockchain with a two-way bridge.
Example- Polygon POS chain.
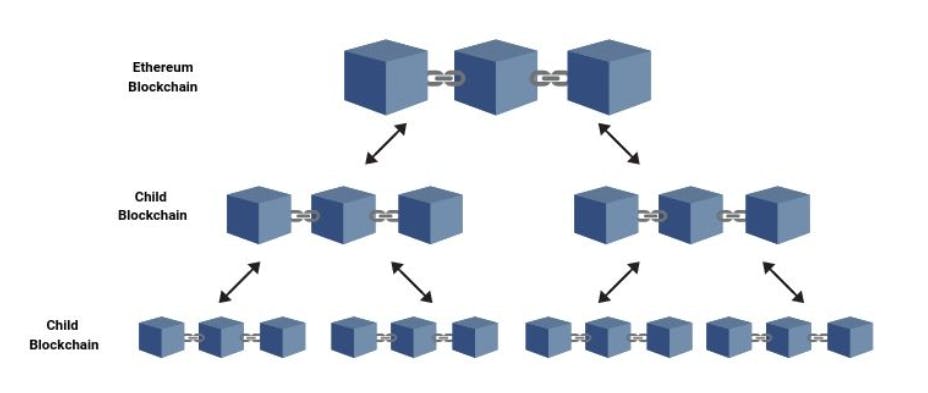
- Plasma: A Plasma chain is a separate blockchain anchored to Ethereum Mainnet but executing transactions off-chain with its own mechanism for block validation. Plasma chains are sometimes referred to as "child" chains, essentially smaller copies of the Ethereum Mainnet.
- Validium: A Validium chain uses validity proofs like zero-knowledge rollups but data is not stored on the main layer 1 Ethereum chain.
In the next blog, we will discuss Sharding in detail and learn about how it can solve the existing problem.
To understand Layer 2 with video you can watch the below video.
For Rollups you can watch :-
Thank you for reading this blog it means a lot. I hope you understand Scaling solutions for Ethereum.
Feel free to comment with your thoughts, suggestions, and what you want me to include. :)
Thank you!