Bigger picture of Working of Blockchain
- Blockchain is the chain of Blocks.
- A single block contains :-
- Data of that block.
- Hash value of that block.
- Hash value of the previous block.
Properties we achieve through Blockchain :-
- Decentralization
- Immutability
- Indestructible
- Transparency
How we achieve these properties :-
Decentralization :-
- Every node present in blockchain ecosystem have a copy of blockchain and no single authority controls the ecosystem.
- There are significant examples of problems with centralization - a few of which we will list here:
- Data breaches in centralized systems expose a lot of data.
- Centralized authorities can censor and shut down speech. (If you don't know what is node please read my previous blogs on a blockchain)
- By storing data in a peer-to-peer network of nodes, we achieve decentralization in blockchain.
Immutability :-
- Data on the blockchain is immutable. We cannot modify the data on a blockchain.
- Block contains hash value previous block so if we change or modify the in any block of blockchain we need to mine all the blocks afterward because the hash value will be changed and nonce also change and all blocks are connected in a chain.
- Also we need to mine that many blocks on more than 50% of nodes present in the ecosystem. (more than 50% because the majority will have one kind of chain and only that is acceptable)
- So this process is nearly impossible to do.
- Hence we achieve immutability in the blockchain.
- More the nodes more secure the blockchain is.
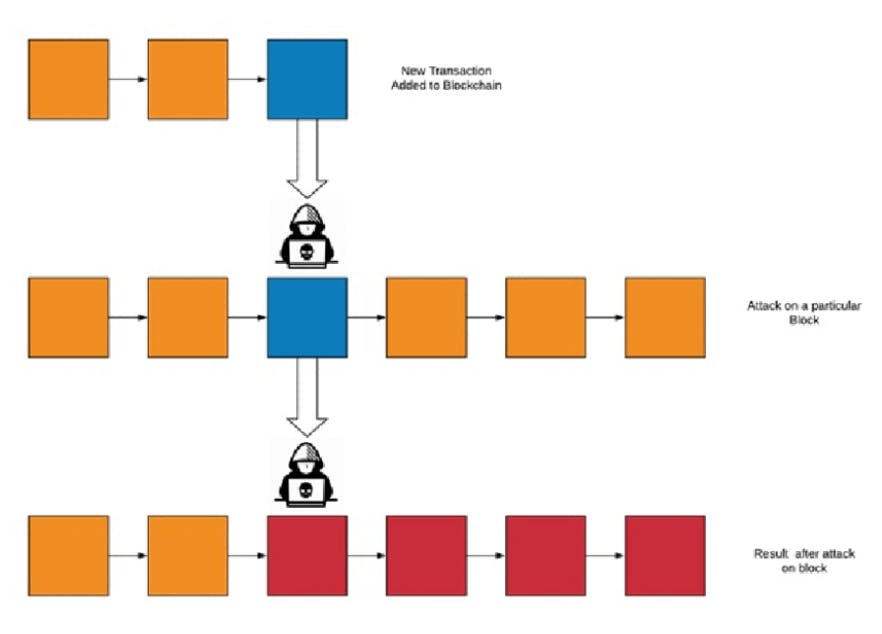
Indestructible :-
- As mentioned above blockchain works on decentralization principle.
- In a centralized system it is very easy to destruct the system we have to only disturb the central system then the whole system will stop.
- But in blockchain to stop the ecosystem we need to stop each and every node.
- If a single node is running then also it works perfectly fine.
- Till now it is nearly impossible to destruct every node at the same time.
- Hence we achieve indestructibility in the blockchain.
- More the number of nodes more the indestructibility.
Transparency :-
- Every transaction is stored on the blockchain and we can get all the information of any transaction easily.
- Hence transparency is maintained on blockchain.
- If your data is private and you do not want to share it on Public Blockchain you can create your own blockchain Private Blockchain.
- But in Private Blockchain, you may face the issue of Immutability.
- Now let's talk about this issue.

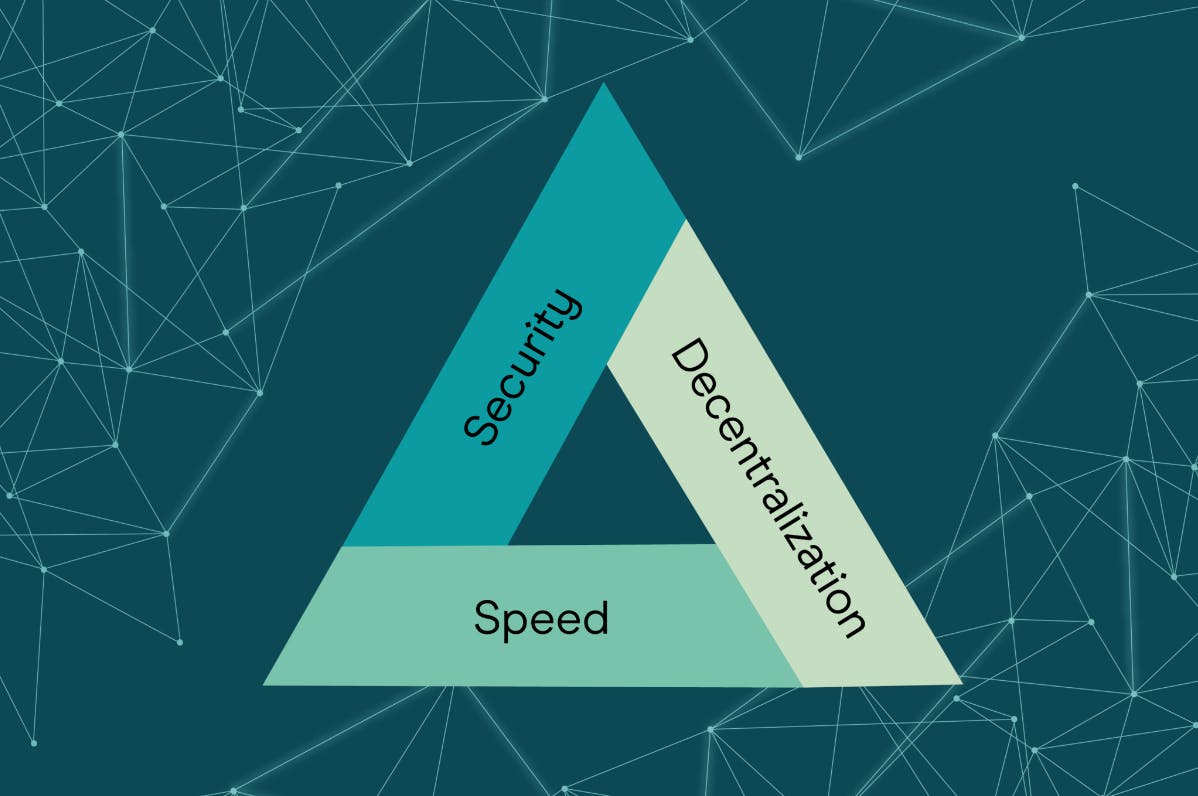
Trilemma of Blockchain
- Decentralization
- Security
- Scalability
- The Blockchain Trilemma refers to a widely held belief that decentralized networks can only provide two of three benefits at any given time with respect to decentralization, security, and scalability.
- While blockchain technology is proving its remarkable utility in industries ranging from finance to art, the underlying structure of decentralized networks comes with unique challenges when compared to centralized networks.
- As early as the 1980s, computer scientists developed what’s called the CAP theorem to articulate perhaps the most major of these challenges. According to the CAP theorem, decentralized data stores — of which blockchain is an iteration — can only provide two of three guarantees simultaneously: consistency, availability, and partition tolerance (CAP).
- In the context of modern distributed networks, this theorem has evolved into the Blockchain Trilemma — the popular belief that public blockchains must sacrifice either security, decentralization, or scalability.
Example:
- While Bitcoin is decentralized and secure, it is only able to process approximately seven transactions per second (TPS).
- Enterprise blockchains like Hyperledger’s Fabric are secure and can handle high transactional throughput, but are centralized, with a highly limited number of consensus-achieving nodes.
Blockchains that are fast and decentralized — but more insecure — are vulnerable to hacks that are untenable in the long term.
- A global community of businesses, start-ups, and technologists are feverishly developing Layer-1 and Layer-2 solutions that are solving this Blockchain Trilemma.
- In the next blog we will discuss the solutions for Trilemma.
Must Watch the video for working of Blockchain :- YouTube Video
Article on Blockchain Trilemma :- Article
Thank you for reading this blog it means a lot. I hope you understand working of Blockchain. In upcoming blogs I will share Solution for Trilemma .
Feel free to comment with your thoughts, suggestions, and what things you want me to include. :)